Syntactic parsing¶
lambeq’s string diagrams are based on a pregroup grammar to keep track of the types and the interactions between the words in a sentence. When a detailed syntactic derivation is required (as in the case of DisCoCat), a syntax tree needs to be provided by a statistical parser. However, since the pregroup grammar formalism is not particularly well-known in the NLP community, there is currently no wide-coverage pregroup parser that can automatically provide the syntactic derivations. To address this problem, lambeq provides a passage from a derivation in the closest alternative grammar formalism, namely Combinatory Categorial Grammar (CCG), to a string diagram which faithfully encodes the syntactic structure of the sentence in a pregroup-like form [YK21]. Due to the availability of many robust CCG parsing tools, this allows the conversion of large corpora with sentences of arbitrary length and syntactic structure into pregroup and DisCoCat form.
Since Release 0.2.0, the standard lambeq installation includes a state-of-the-art CCG parser based on [Cla21], fully integrated into the toolkit. This parser is provided under the name Bobcat. Additionally, lambeq implements a detailed interface in the text2diagram package that allows connection to one of the many external CCG parsing tools that are currently available. For example, lambeq is also shipped with support for depccg [1] [YNM17], a fast parser that comes with a convenient Python interface.
Additional external parsers can be made available to lambeq by extending the CCGParser class in order to create a wrapper subclass that encapsulates the necessary calls and translates the respective parser’s output into CCGTree format.
Finally, for users who prefer to keep the installation of the toolkit light, lambeq also includes a web-based parser class that sends parsing queries to an online API, so that local installation of a full CCG parser is not strictly necessary anymore – although strongly recommended for most practical uses of the toolkit.
Reading CCGBank¶
The CCG compatibility makes immediately available to lambeq a wide range of language-related resources. For example, lambeq features a CCGBankParser class, which allows conversion of the entire CCGBank corpus [2] [HS07] into string diagrams. CCGBank consists of 49,000 human-annotated CCG syntax trees, converted from the original Penn Treebank into CCG form. Having a gold standard corpus of string diagrams allows various supervised learning scenarios involving automatic diagram generation. Fig. 3 below shows the first tree of CCGBank‘s Section 00 converted into a string diagram.
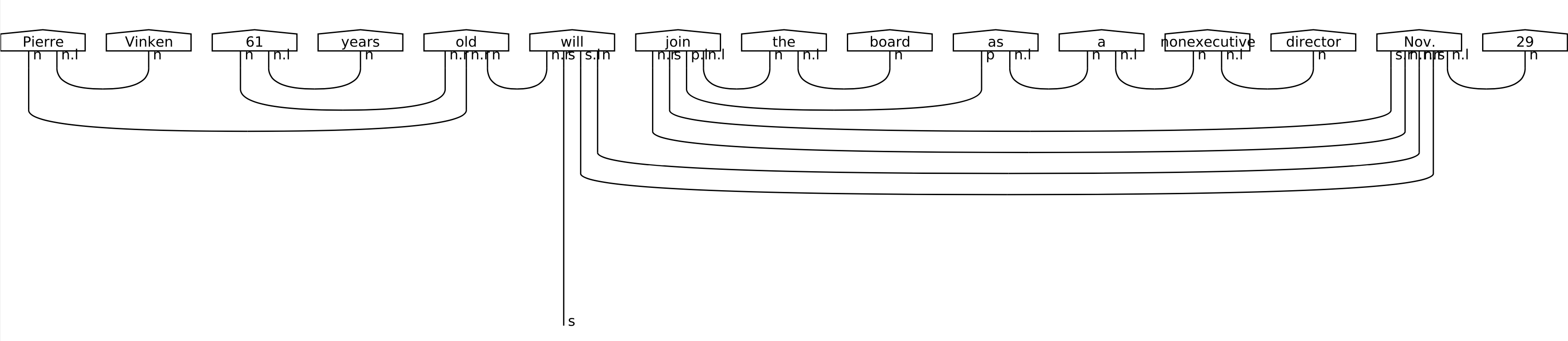
Fig. 3 The first derivation of CCGBank as a string diagram.¶
Footnotes